2C - Intermolecular forces
|
2C - Intermolecular forces |
|
1) Describe how Van der Waals' forces arise. [6]
Electrons in shells are continually moving [1] the electrons are continually fluctuating [1]
this creates an uneven distribution of electrons [1] which sets up an instantaneous dipole [1]
this induces a dipole in neighbouring atoms / molecules [1] creating weak forces of attraction [1]
2) Arrange the elements of Group 0 in order of increasing boiling points. Explain your answer. [4]
He, Ne, Ar, Kr, Xe, Rn [1] As you go down the Group, the atoms have more electrons [1]
which gives a greater uneven distribution of electrons [1]
giving stronger instantaneous dipole - induced dipole forces of attraction [1]
3) Which of the following have hydrogen bonding: [6]
| a) H2S | b) CH4 | c) CH3OH | d) NO2 | e) CH3NH2 | f) PH3 | |
| No | No | Yes | No | Yes | No |
4) Draw diagrams of hydrogen bonding between the following molecules. Include any dipoles:
a) 2 molecules of water [2] Labelled bond between LP and H [1] Dipoles shown [1]
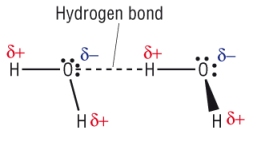
b) 2 Molecules of ammonia [2]
Labelled bond between LP and H between the 2 molecules [1] Dipoles shown [1]
c) 1 molecule of water and 1 molecule of ammonia [2]
Labelled bond between LP and H [1] Dipoles shown [1]
5) State 3 anomalous properties of water and explain each property: [6]
Unusually high melting / boiling point [1] H bonding is strongest IMF, more energy needed to overcome [1]
Ice less dense than water [1] H bonds are longer than covalent bonds [1]
Surface tension [1] extensive H bonds across the surface of water [1]