2C - Bonding and structure review /39
|
2C - Bonding and structure review /39 |
|
1) Arrange the elements of Group 7 in order of increasing boiling points. Explain your answer. [4]
Down the group [1] As you go down the Group, the molecules have more electrons [1]
which gives a greater uneven distribution of electrons [1]
giving stronger instantaneous dipole - induced dipole forces of attraction [1]
2) Describe how Van der Waals' forces arise. [6]
Electrons in shells are continually moving [1] the electrons are continually fluctuating [1]
this creates an uneven distribution of electrons [1] which sets up an instantaneous dipole [1]
this induces a dipole in neighbouring atoms / molecules [1] creating weak forces of attraction [1]
3) State whether the following molecules are polar or non polar: [7]
a) Define electronegativity [1]
The power of an atom in a molecule to attract bonding pair electrons towards itself [1]
| b) H2S | c) CH4 | d) CH3OH | e) I2 | f) CH3NH2 | g) PH3 | |
| Polar | Non polar | Polar | Non polar | Polar | Polar |
4) State the type of intermolecular forces that exist between the following molecules: [6]
| a) H2S | b) CH4 | c) CH3OH | d) I2 | e) CH3NH2 | f) PH3 | |
| PD - PD | VDW | H - B | VDW | H - B | PD - PD |
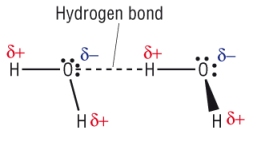
5) Draw intermolecular force between 2 molecules of water. Include any dipoles [2]:
Labelled bond between LP and H [1] Dipoles shown [1]
6) Describe metallic bonding and use your diagram to explain whether it conducts electricity.
You may wish to use a diagram. [3]

Labelled diagram [1] electrostatic forces of attraction between delocalised electrons and metal ions [1]
The electrons are free to move [1]
7) Discuss the conductivity of ionic compounds compared with simple covalent structures. Explain your answer. [6]
Ionic: Solids do not conduct [1] as the ions are held in a fixed position [1]
Dissolved [1] and molten [1] as the ions are free to move [1]
Covalent: Does not conduct electricity as there are no free moving charges [1]
8) With the aid of diagrams discuss and explain the solubility of sodium chloride and Iodine in water. [5]
Ionic diagram of both ions surrounded by water molecules [1] Water is a polar molecule [1]
These are attracted to the ions, weaken the ionic bonds pulling them away from the lattice [1]
Iodine is a non polar molecule [1] which is too weak to break the hydrogen bonds in water [1]