2B - Review

|
2B - Review |
 |
1. This question is about different models of bonding and molecular shapes. Magnesium sulfide shows ionic bonding.
(i) What is meant by the term ionic bonding? [1]
(ii) Draw a dot-and-cross diagram to show the bonding in magnesium sulfide. Show outer electron shells only. [2]
2. Dot-and-cross diagrams can be used to predict the shape of covalent molecules.
Fluorine has a covalent oxide called difluorine oxide, F2O. The oxygen atom is covalently bonded to each fluorine atom.
(i) Draw a dot-and-cross diagram of a molecule of F2O. Show outer electron shells only. [2]
(ii) Predict the bond angle in an F2O molecule. Explain your answer. [3]
3. Chemists have developed models for bonding and structure which are used to explain different properties.
Ammonia, NH3, is a covalent compound.
(i) Explain what is meant by a covalent bond. [1]
(ii) Draw a dot-and-cross diagram to show the bonding in NH3. Show outer electrons only. [1]
(iii) Name the shape of the ammonia molecule and explain, why ammonia has this shape and has a bond angle of 107°. [3]
4. Molecules of NCl3 have a bond angle of 107°.
(i) Name the shape of an NCl3 molecule. [1]
(ii) Explain why a molecule of NCl3 has this shape and a bond angle of 107°. [3]
5. Antimony is in Group 5 of the Periodic Table. It forms a compound with hydrogen that has the formula SbH3.
(i) Predict the bond angle in SbH3. [1]
(ii) Explain why a molecule of SbH3 has this bond angle. [2]
6. The dot-and-cross diagram of an ammonia molecule is shown below.
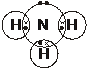
Predict, with reasons, the bond angle in an ammonia molecule. [4]