2C - Polarity - VDW or Permanent Dip - Dip IMF
|
2C - Polarity - VDW or Permanent Dip - Dip IMF |
|
1) Draw the shapes of the following molecules showing any polar covalent bonds.
Show any dipoles on the diagrams: [6]
| a) | H - H | b) | Cl - Cl | c) | d+ H - Cl d- | d) |
 |
e) |
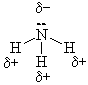 |
f) |
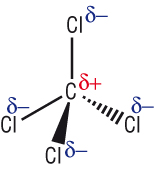 |
2) For the molecules in (1), state whether the molecule is 'polar' or 'non - polar'. [6]
| a) | Non - Polar | b) | Non - Polar | c) | Polar | d) | Polar | e) | Polar | f) | Non - Polar |
3) Draw dot and cross diagrams for the following pairs of molecules: [4]
| a) |
 |
 |
| b) |
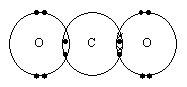 |
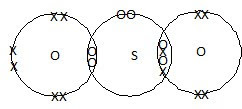 |
c) For each of the above pairs, predict and sketch the shapes and show any dipoles. [2]
| a) |
 |
 |
|
| c) |
 |
 |
|
| d) | Non - Polar - Although the bonds are polar, the molecule is symmetrical. It does not have a d+ / d- end to the molecule | Polar - The bonds are polar, and the molecule is not symmetrical. It has a d+ / d- end to the molecule | |
| b) |
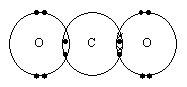 |
 |
|
| c) |
|
 |
|
| d) | Non - Polar - Although the bonds are polar, the molecule is symmetrical. It does not have a d+ / d- end to the molecule | Polar - The bonds are polar, and the molecule is not symmetrical. It has a d+ / d- end to the molecule |
4) Using your answers above, determine which intermolecular forces exist between the following molecules.
Van der Waals or Permanent dipole - dipole interactions: [10]
a) H2 VDW b) Cl2 VDW c) HCl PD - PD d) H2O PD - PD e) NH3 PD - PD
f) CCl4 VDW g) BF3 VDW h) PF3 PD - PD i) CO2 VDW j) SO2 PD - PD
5) What is the pattern between Qu2,3 and Q4. [2]
Non - polar molecules have VDW
Polar molecules have PD - PD